What is a Programmable Logic Controller, or PLC?
If you’ve used a computer, and you’ve used an Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or any number of other microcontrollers, you might think that a computer based on the physical world is a relatively new concept. A digital input causes some sort of conditional logic to make something blink, your robot to move, a signal to be transmitted, or any number of other things.
This type of logic has, in fact, been going on for quite some time in industry. In 1968, a man named Richard E. Morley proposed the Modular Digital Controller (MODICON) to a car manufacturer. This MODICON, or programmable logic controller (PLC), was used to replace complicated relays with virtual programmable relays, making machinery changes in industry much, much faster.
This later became the commercial MODICON 084, which led to many more manufacturers making their own version. Here’s an article on the history of the PLC if you’d like more background.
How do You Program One?
Computers and microcontrollers that you may be familiar with use a typed programming language to let them perform their tasks. You might assume, as I did when I first learned to program in this fashion, that a PLC uses something similar, like C, BASIC, or Python. It doesn’t (at least not in its most basic form); instead, it uses something called “ladder logic.”
This ladder logic looks exactly like it sounds, with a ladder-like screen with characters like “X1″ with a normally open contact connected to an output labeled as, say “Y0″ at the end of it. These ladder “rungs” are suspended between two rails which represent electrical power. Thus an electrician with a background in setting up relay logic circuits could, in theory, read this code without additional training.
To illustrate this further, if you were to set up a very simple program where if input “X1″ is on, then output “Y0″ turns on, it would be drawn like this:

There are several other ways to program a PLC, like structured text or sequential function charts (and there are many more functions than what I’ve listed above), but ladder logic is the most commonly used from my experience.
What are the Advantages?

In industry, the big advantage of a PLC using ladder logic is that, as mentioned earlier, a technician can, in theory, read the code like an electrical diagram. Sometimes they may have access to make changes, but when they don’t, there is at least some semblance of logic to what’s going on to non-programmers.
The other huge advantage is that they are extremely robust. Most have input/output cards that can be changed separately from the processor itself, and I have never seen the processor itself fail that I’ve been in charge of. OK, fail on its own is more accurate; I did shock one to death, but that was certainly no fault of its own.
If you’re making something for your use or some sort of prototype (like most Makers are), you expect to have to fiddle with your electronics to some degree. If you’re designing a machine that makes the company you work for millions of dollars each year, you absolutely don’t want any electrical issues getting in the way. Multiply this by all of the machinery in your plant (dozens or hundreds of PLCs) and you really don’t want to have to look at them every day.
Why don’t Makers Use Them More?
The reason, in my opinion, that PLCs aren’t used in home projects more is cost. A full PLC with input, output, and any number of other cards (Ethernet for example) can easily cost thousands of dollars. Add another couple thousand for an HMI (human machine interface touch screen) and, in many cases, more money for the programming software, and you have something that is well out of most Maker budgets.
Additionally, size can be a hindrance to implementing this type of control. Even most small PLCs are much larger than an Arduino board. This is not generally a problem in industry, but it doesn’t work well for a robot that measures a few inches in each dimension.
How Can I learn about Them?
I’m a mechanical engineer and have a good amount of experience with PLC programming. I’ve programmed a dozen or so machines from scratch and troubleshot many more. Although I had some limited programming experience when I started, ladder logic was absolutely foreign to me to begin with. From talking to electrical engineers in industry, they generally have no education on this particular programming style in the beginning either.
That being said, if you one day want to program production machinery in an engineering role, most likely you will learn it on the job. For this, a good internship is an excellent thing to have. I learned an incredible amount during my “co-op” semesters about electronics as well as mechanical stuff that helps me make interesting things to this day.
On the other hand, if I’m doing a project at home, most likely I’m still going to be using some sort of “Maker-class” board. For something like Battlebots, however, where durability is king, I might go for a PLC if my budget was large enough.
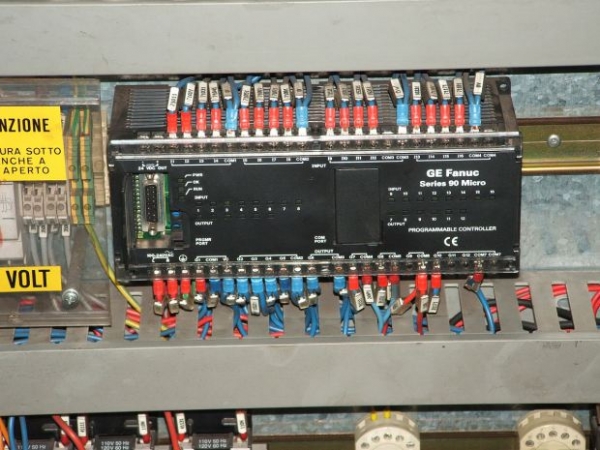
Bonus question, what type of PLC was I thinking of when I diagrammed the ladder with X1 and Y1?